Endpoint management is a term I came across relatively recently at a Symantec event – it refers to software used to manage client computers, laptops, and servers in an organisation (the endpoints of the network). Endpoint management software does things like automating the rollout of updates, manages licensing of software and often has a role in energy management of computers (ensuring they are shut down at the end of the day, not consuming resources when not in use). Also, policies can be set to ensure the power management of the machines doesn’t interfere with the installation of any patches.
With the increasing numbers of smartphones and tablets entering the workplace, a new class of enterprise software is appearing, mobile endpoint management. I’ve had discussions with Symantec about this last year and had a demo of IBM’s beta Mobile Endpoint Manager at this year’s IBM Pulse.
The IBM software, while not yet released, is still quite interesting. It has a considerable amount of functionality for securing devices and their data, as well as what IBM are calling micro-vpn – a nifty little bit of coding which allows for the ability to VPN from within an individual app on the mobile device.
One obvious trick that’s being missed though? Energy management for mobile devices.
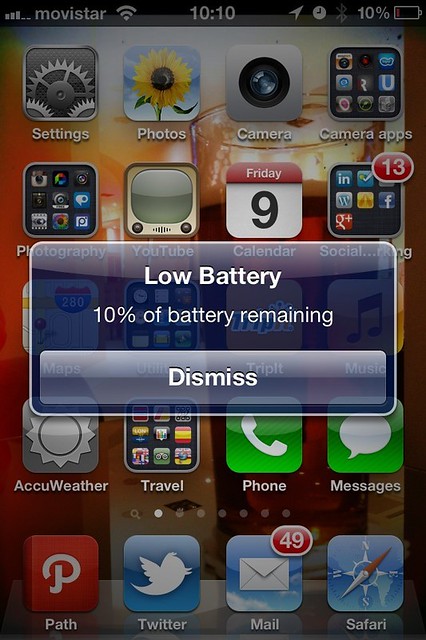
The one issue that all smart phone owners share is battery life. This is also an issue for organisations which provide smartphones to their staff because many of those employees will charge their phones while at work, increasing the organisations’ energy and carbon footprints. Potentially worse though, is if the battery does run out, the staff member in question is harder to contact and may be cut off from company resources.
How do you, through software, extend the life of a smartphone battery?
Well, off the top of my head, a few things come to mind – how about scanning for services not being used and shutting them down (bluetooth, wi-fi, even 3G if battery life becomes critical). Also, applications not being used could be automatically force-quit so they aren’t consuming resources in the background. Shutting off notifications (and iCloud on iPhones to avoid unnecessary uploading of data.
All of this could be configured to kick in as the amount of battery life remaining dwindles. At 30% shut off notifications and Bluetooth, at 25% iCloud and any open, but unused apps, and so on.
Another opportunity for saving comes from poorly coded applications which consume power when they are supposed to be doing nothing in the background – the iPhone Skype app had this issue for a while. An intelligent Endpoint Management app would monitor all apps energy use on the phone and report anomalous use to the user, along with an offer to close it (and potentially even offer to report the issue back to Apple and/or the app developer).
If this is reported transparently to the phone user, with an option of an opt-out, and with estimates of the amount that this will extend the battery life, most people will buy into it very quickly.
And it saves money, energy, and carbon emissions. Win, win and win.
Anyone coding Mobile Endpoint Management and not considering energy management is missing a trick.
Photo Credit Tom Raftery
Follow @TomRaftery