Photo credit NASA Goddard Photo and Video
Is the massive environment, health and safety (EHS) risks, which fossil fuel companies represent, starting to hurt their businesses?
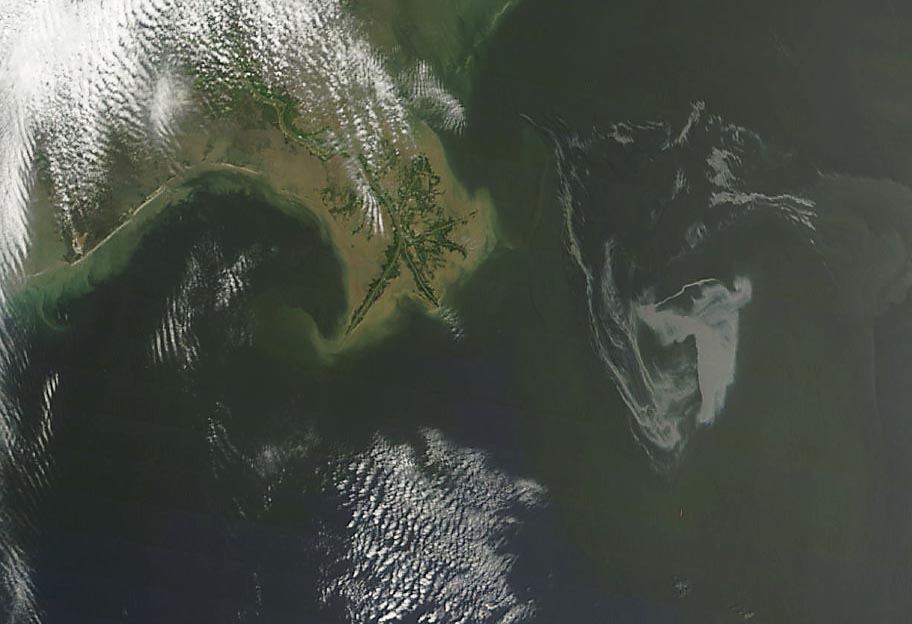
Reading this morning about the Deepwater Horizon explosion and the continuing oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico I note that BP’s market value has fallen from ?122bn last week to ?102.5bn today – a loss of almost ?20bn in a week (or just over 16% of its value).
What has to be really worrying for BP investors is that
- Oil from the oil spill reached the Louisiana coast by April 30th
- Analysts estimate that the Louisiana fishing industry could sustain $2.5 billion in losses, while Florida could lose $3 billion in tourism income
- The oil spill could be leaking at a rate of 25,000 barrels a day, five times the government’s current estimate, industry experts say
- No one can say for sure when it will finally stop but estimates are that it will take up to three months and possibly more
- President Obama himself has declared “BP is responsible for this leak. BP will be paying the bill.” and he’s just talking about the cleanup operations, not the litigation
- Documents have emerged showing BP argued against new, stricter safety rules proposed last year by the U.S. agency that oversees offshore drilling, a whistleblower is accusing BP of failing to keep key documents vital to safe shut-down on its Atlantis rig and
- the first of the court cases against BP are already being filed
Things must be pretty grim at present in BP’s plush London HQ but it is not like BP have an exceptionally poor record by fossil fuel producers standards. For example:
- Gulf Oil (now Chevron) and Total S.A. were found jointly responsible for the explosion at the Bantry Bay oil terminal which killed 50 people in 1979
- ExxonMobil has an appalling environmental record which includes the Exxon Valdez oil spill in Alaska, the Booklyn oil spill, the Sakhalin-I oil and gas project in the Russian Far East and accusations that it knowingly assisted human rights violations, including torture, murder and rape
- Shell has a similarly poor environmental record being heavily invested in oil extraction from Canadian tar sands, and Shell has been accused of human rights violations in Nigeria, including summary execution, crimes against humanity, torture, inhumane treatment and arbitrary arrest and detention
- Chevron’s environmental and human rights record is, frankly, appalling.
And this EHS risk is not limited to oil and gas companies. On the contrary:
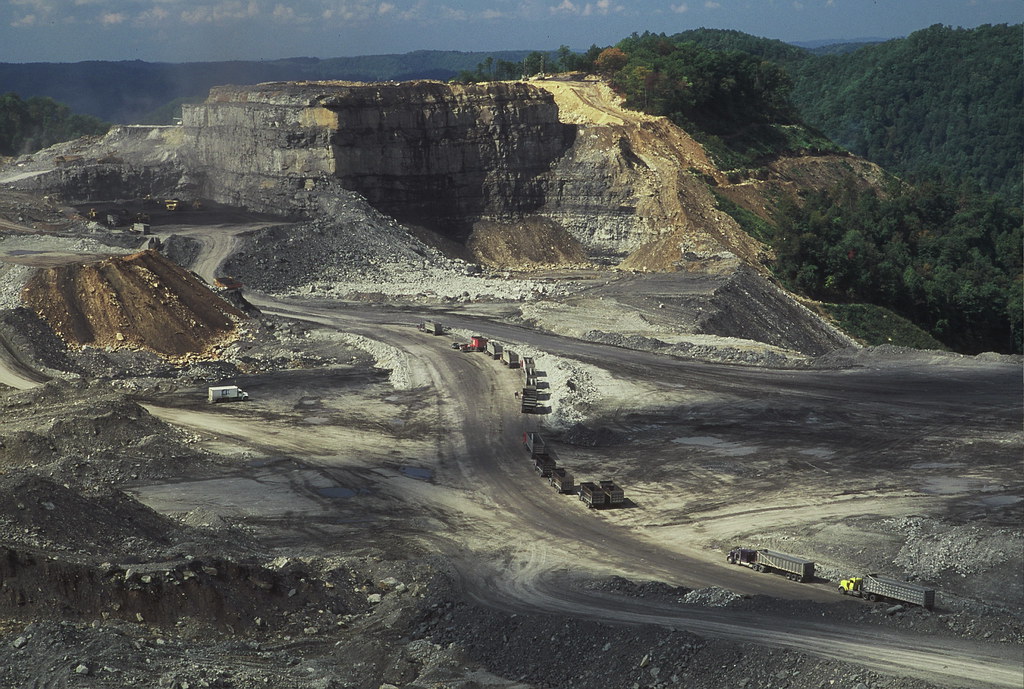
Massey Energy, the owner of the Upper Big Branch coal mine which exploded four weeks ago, killing 29 miners, has a terrible record of environmental and health and safety abuses. In fact, so bad are they that the FBI announced recently that they would be investigating Massey for the possible bribery of federal officials overseeing mining industry regulation and for potential criminal negligence.
Massey’s main competitors in the US are little better –
- Arch Coal, and CONSOL Energy are heavily involved in Mountaintop Renewal while
- Peabody Energy has a long history of of opposing efforts to mitigate the negative environmental effects of coal production and combustion
With the rapidly increasing number of environmental lawsuits taking place companies like the above are going to be spending more and more of their time in the courts with the consequent losses in time, productivity and reputation which that entails.
When you couple that with the growing interest in environmental issues being taken by the SEC, the EPA and investors and suddenly the business case for being an ethical, non-polluting business seems all the stronger.
After all, as many people noted on Twitter in the last few days, spills of air from wind farms or sun from solar plants are not going to have the devastating environmental consequences we have witnessed in the last decades as a result of our addiction to fossil fuels.
You should follow me on twitter here.