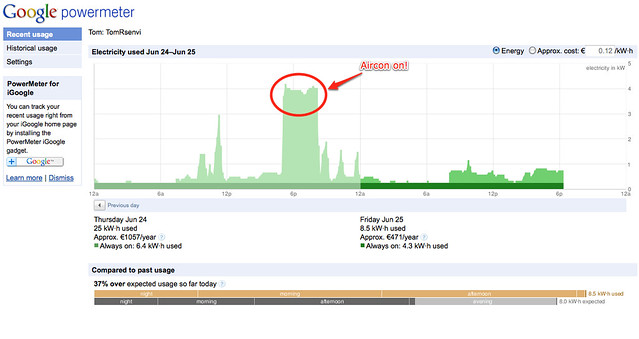
Last week Google announced that it was shutting down its PowerMeter application (a screenshot of which is above). A couple of days later Microsoft divulged that it was closing its PowerMeter competitor, Microsoft Hohm.
This is very disappointing because the two products were decidly disruptive and, as Google mentioned, studies show that having simple access to energy information helps consumers reduce their energy use by up to 15%. Both services cited lack of uptake as the reason for their termination.
In Microsoft’s case, there is a very good reason why this was so, it never opened up Hohm beyond the US – if you only allow 4% of the world’s population access to your application, you can’t really claim to be surprised if you don’t see significant uptake.
PowerMeter though, in its announcement said –
our efforts have not scaled as quickly as we would like, so we are retiring the service
Why then did Google’s PowerMeter not scale, despite being open to all comers?
Simply because Google were too early to market, I suspect.
Being a trailblazer meant that getting data into PowerMeter was not trivial. The only way to make it easy for data entry would have been if Google managed to sell its services to utility companies but Google had very little success with this approach. Why would utility companies allow Google access to their customer usage data? That was never a runner.
The alternative was to use a device like a CurrentCost – an in-home energy meter which had the ability to upload its data to PowerMeter. However, as I detailed in this post, there were multiple problems with the CurrentCost meters which meant they were never a reliable option for PowerMeter data entry.
Obviously, if you can’t get your data into PowerMeter, it is not going to be of much use to you.
The need for real-time energy information is obvious. It is very difficult to identify wasteful electricity practices when you receive your consumption information (i.e. your bill) up to two months after you used it.
So what now?
Well, it looks like we are back to getting this information from our utility companies. Things are changing (albeit at a glacial pace) on that front though. As I mentioned in my post on Centrica’s Smart Meter Analytics implementation, the technological barriers to rolling out a compelling home energy management have come way down.
Now if utility companies actually roll out energy management applications properly, we could see significant reductions in wasteful energy use.
Photo credit Tom Raftery