We attended this year’s SapphireNow event (SAP’s customer and partner conference) in Orlando and were very impressed with some of the advances SAP and their ecosystem are making in the field of healthcare.
Why is this important?
Healthcare for many decades now has been stagnant when it comes to technological disruption. Go to most hospitals today and you will still see doctors using paper and clipboards for their patient notes. Don’t just take our word for it, in her highly anticipated 2015 Internet Trends report Mary Meeker clearly identified that the impact of the Internet on healthcare is far behind most other sectors.
But this is changing, and changing rapidly. The changes coming to the healthcare sector will be profound, and will happen faster than anyone is prepared for.
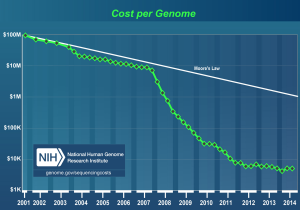
And one of the main catalysts of this change has been the collapse in the cost of gene sequencing in the last ten years. See that collapse charted in the graph to the right. And note that the y-axis showing the cost of sequencing is using a logarithmic scale. The costs of sequencing are falling far faster than the price of the processing power required to analyse the genetic data. This means the cost of sequencing is now more influenced by the cost of data analysis, than data collection. This has been a remarkable turn of events, especially given the first human genome was only published fourteen years ago, in 2001.
The advances in the data analytics picking up pace too. In memory databases, such as SAP’s HANA, and cognitive computing using devices like IBM’s Watson, are contributing enormously to this.
To get an idea just how much the analytics is advancing, watch the analysis of data from 100,000 patients by Prof Christof von Kalle, director of Heidelberg’s National Center for Tumor Diseases in the video below. Keep in mind that each of the 100,000 patients has 3bn base pairs in their genome, and he’s analysing them in realtime (Prof Von Kalle’s demo starts at 1:00:03 in the video, and lasts a little over 5 minutes).
As he says at the conclusion, two years ago a similar study conducted over several years by teams of scientists was published as a paper in the journal Nature. That’s an incredible rate of change.
IBM are also making huge advances in this field with their cognitive computing engine, Watson. In a recent announcement, IBM detailed how they have teamed up with fourteen North American cancer institutes to analyse the DNA of their patients to gain insights into the cancers involved, and to speed up the era of personalised medicine.
Personalised medicine is where a patient’s DNA is sequenced, as is the DNA of their tumour (in the case of cancer), and an individualised treatment, specific to the genotype of their cancer is designed and applied.
This differs from the precision medicine offerings being offered today by Molecular Health, and discussed by Dr Alexander Picker in the video at the top of this post.
Precision medicine is where existing treatments are analysed to see which is best equipped to tackle a patient’s tumour, given their genotype, and the genotype of their cancer. One thing I learned from talking to Dr Picker at Sapphirenow is that cancers used to be classified by their morphology (lung cancer, liver cancer, skin cancer, etc.) and treated accordingly. Now, cancers are starting to be classified according to their genotype, not their morphology, and tackling cancers this way is a far more effective form of therapy.
Finally, SAP and IBM are far from being alone in this space. Google, Microsoft and Apple are also starting to look seriously at this health.
With all this effort being pored into this personalised medicine, I think it is safe to say Ms. Meeker’s 2016 slide featuring health will look a little different.
UPDATE – Since publishing this post SAP have uploaded a video to YouTube showcasing their internal application of Molecular Health’s solution for employees of SAP who are diagnosed with cancer. You can see that below:
Full disclosure – SAP paid my travel and accommodation to attend their Sapphirenow event