GreenWave Reality are an energy management company who came out of stealth last week to announce they had just landed an $11m equity round and to announce its new Energy Management Platform (although EMP is an unfortunate acronym in this context!).
The company’s executive team is made up mostly of former execs of Cisco’s Consumer Business Group – so not only have they worked closely, successfully in the past, they also have experience producing consumer electronics and its advisory board reads like a who’s who of the CE industry.
So what does GreenWave Reality’s Energy Management Platform actually consist of?
Well, at its most simple, it is a home area network containing:
- smart plugs (power nodes) which are accessible wirelessly
- a gateway which communicates wirelessly with the power nodes (and in time with smart LEDs, EV’s, etc.), with your utility, and with GreenWave’s data center and
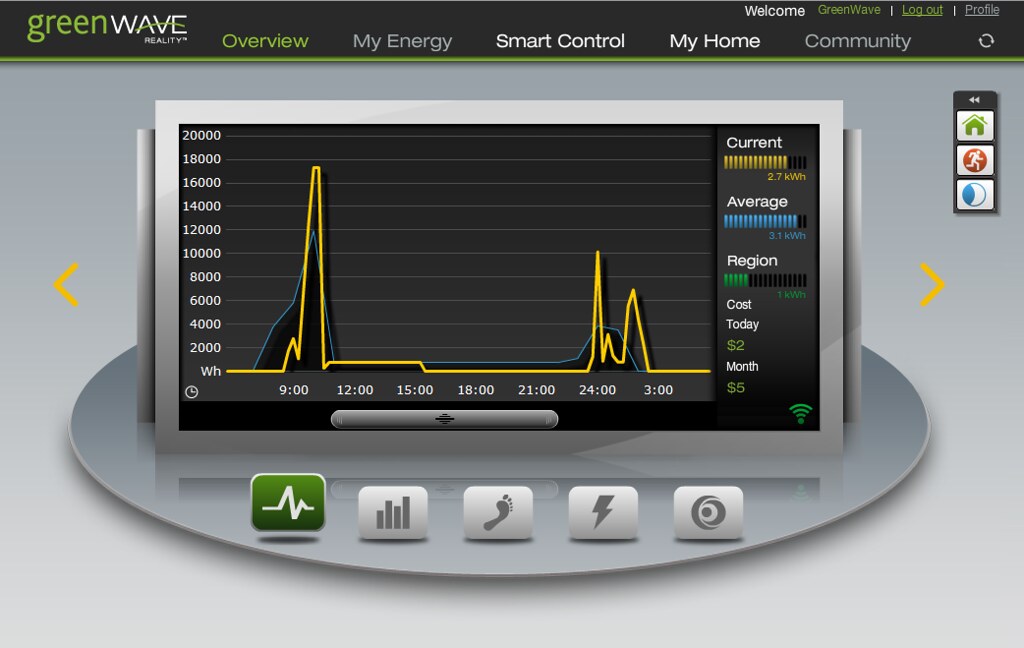
- a highly configurable wireless display which not just reports on energy consumption, but can also control connected devices in the home
GreenWave see utility companies as the customers for their platform, with the utilities distributing the products to their residential consumers. With retail utility companies under increasing pressure to reduce their emissions, products like this are bound to pique their interest.
The fact that the data from GreenWave’s Gateway product is transmitted back to GreenWave’s data center enables GreenWave to provide access to a home energy portal for consumers via the Internet. In this way, connected appliances are controllable, not just from the in-home wireless display, but from anywhere with Internet access, even a smart phone. Perfect for those times when you are out and wondering if you remembered to turn off the lights/TV/whatever!
On the flipside, this raises obvious privacy issues I’d like to see addressed via a Privacy Policy page on the GreenWave site, at the very least.
This will also enable home-owners to compare their energy use with the average use for others in their area to see whether they are energy hogs, or Greener than their average neighbour.
GreenWave is going the standards only route (ZigBee, ZWave, etc) so if consumers have already invested in (or are thinking of buying) devices which use these protocols, they’ll be readily accessible on the platform.
Finally, Speaking to GreenMonk ahead of the company?s launch GreenWave told us that they are launching a Smart dimmable LED light later this year which as well as being extremely energy efficient, will have a built-in transceiver so that it can be fully controlled by the company’s Energy Management Platform.
I have to say, having spoken to the guys in GreenWave, it does seem like these guys have their ducks in a row. I’m looking forward to seeing how this one plays out.
You should follow me on twitter here.