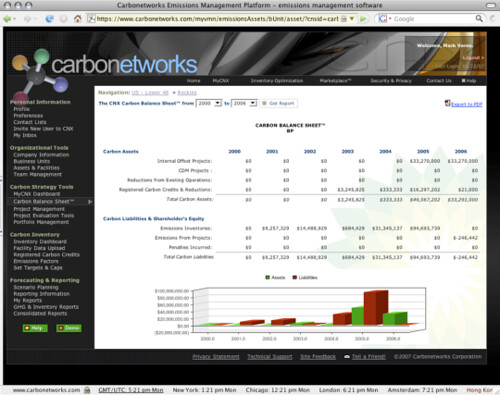
I talked with Carbonetworks’ President and CEO, Michael Meehan, the other day. We discussed Carbonetworks’ Carbon platform, and how their application helps companies participate in global carbon markets.
Carbonetworks software helps companies understand whether their carbon is going to be an asset or liability to them today and in the future as and works with companies to roll out their carbon strategies.
The television image in the video is from videocrab