In my last post I postulated that social software could be used to capture people’s lifestream information and that this could be used by companies to help calculate their carbon footprint.
The case I put forward was more suited for the increasing numbers of people working from home. However, I neglected to point out another painfully obvious example – Dopplr.
Dopplr markets itself as the travel serendipity engine –
Dopplr lets you share your future travel plans privately with friends and colleagues. The service then highlights coincidence, for example, telling you that three people you know will be in Paris when you will be there too. You can use Dopplr on your personal computer and mobile phone. It links with online calendars and social networks.
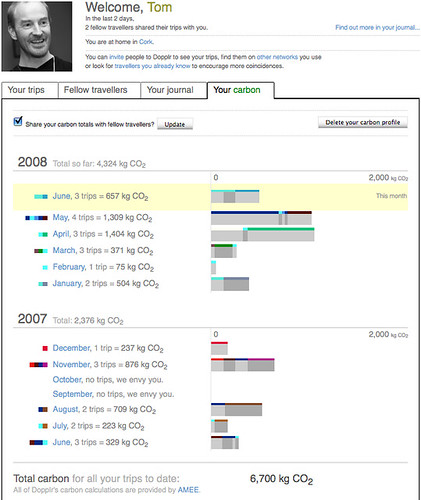
However, potentially far more useful is how Dopplr have teamed up with AMEE (the world’s energy meter) to produce a chart of your travel-related carbon footprint (see the chart above of my travel footprint).
This ties in completely with my earlier post about the potential synergies attainable from combining lifestreaming software and the requirements of carbon accounting.
Can you think of any other use cases for the intersection of lifestreaming and carbon accounting?